Incoterms rules (acronym for International Commercial Terms) are one of the fundamental pillars of international trade. Published and periodically updated by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), Incoterms rules have become essential for clearly defining buyers’ and sellers’ rights and obligations in export and import transactions.
Its most recent version, Incoterms 2020 (effective in 2025), maintains the fundamental principles of transparency, simplicity and adaptability, providing an internationally accepted frame of reference. These rules allow traders to agree on their delivery terms without incurring linguistic or regulatory ambiguities, regardless of country of origin or destination.
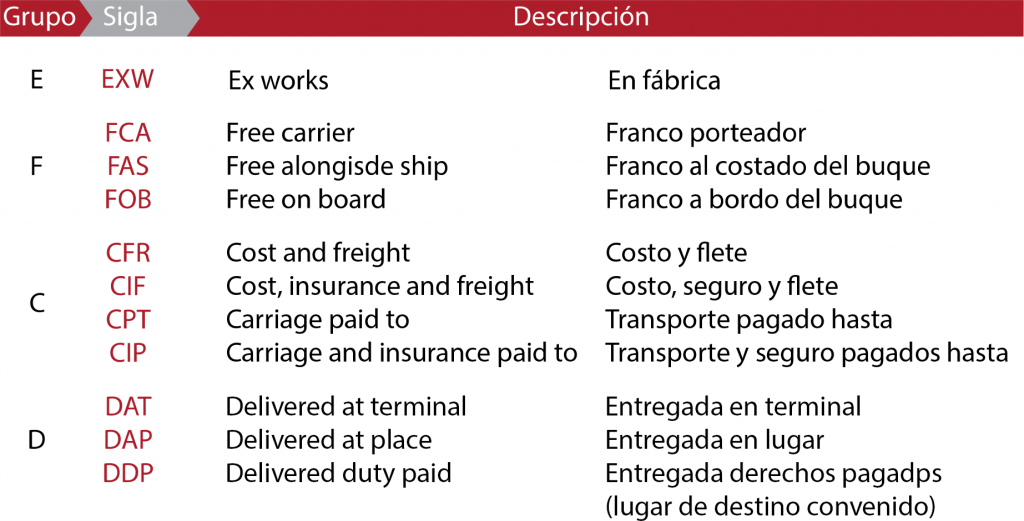
Incoterms
WHAT ARE THE INCOTERMS RULES?
When international trade transactions take place, an aspect that must be clearly established are the conditions regarding the delivery of the goods. A specific location must be agreed upon in as much detail as possible in advance by the seller and purchaser, and it must appear in the international sales contract.
In the contract, the terms under which the goods will be delivered can be established in two ways: by defining as precisely as possible the delivery location, identifying the party responsible for the transport, the party that assumes the risk, the party that must carry out the import and export procedures, etc., all of which must be in several languages; or by using the Incoterms rules.
The Incoterms rules (an abbreviation for International Commercial Terms) are defined by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) in order to contribute to a state of legal security in international transactions for buying and selling goods and for standardising the terms of delivery.
WHAT DO THE INCOTERMS RULES REGULATE?
The purpose of Incoterms rules is to define the rights and obligations of the parties involved in an international transaction for buying and selling goods, and they cover the following five aspects:
- Obligations of the buying and selling parties.
- Costs each party will assume.
- Insurance for the goods.
- Customs
- Time and place for delivery of the goods.
WHAT ASPECTS DON’T THEY REGULATE?
The following aspects remain outside the scope of Incoterms rules, although negotiation of these may be affected by the agreed-upon delivery terms:
- Transfer of ownership of the goods.
- Buying/selling price, payment methods and time periods.
- Applicable regulations in the event of breach of the contract, including its termination and jurisdiction.
- Waiver of liability in relation to the goods.