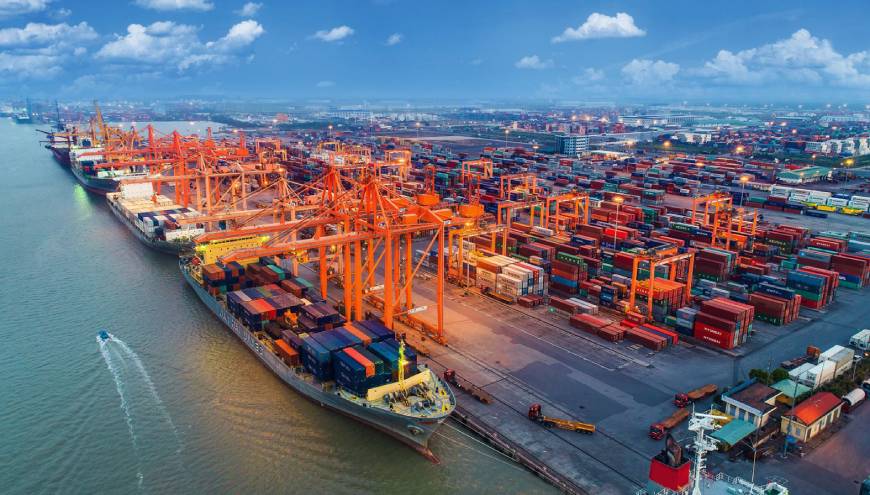
Export to Vietnam
Vietnam has progressively opened up to exporting. Its main trading partners include such powers as the United States, China and Japan. On the other hand, 80% of its imports come from Asian countries, many of which belong to ASEAN. The European Union’s export role vis-à-vis Vietnam is very low, since it accounts for only 5.8% of the Asian country’s total imports.
The Socialist Republic of Vietnam, with an area of 331,000 km2 and a population close to 103 million inhabitants, is a country that despite the covid-19 has maintained an economic growth.
According to the International Monetary Fund, GDP growths were 7.2% in 2019, 2.9% in 2020, 2.6% in 2021 and, also for the World Bank, a GDP increase of between 5.5% and 6% is expected in 2022.
These increases are essentially due to the dynamism of the Vietnamese export sector, which in 2020 generated more than 348 billion US dollars (USM) and, in the same year, ranked 20th in merchandise exports in the world trade ranking, and 19th in terms of imports.
With data from 2020, Vietnam’s current GDP stood at 271,000 USM and per capita income was 10,870 US dollars; while its economic-productive structure is distributed in 41.6% for the service sector, 33.7% in the industrial sector and 14.9% in agriculture.
There are other data that support Vietnam’s positioning on a global scale, such as, for example, the World Economic Forum’s Global Competitiveness Index, which measures how a country uses its resources and its ability to provide its inhabitants with a certain level of prosperity. In 2019, Vietnam ranked 67th in the ranking, which is made up of 141 countries, rising ten positions from the previous year.
Another relevant economic data is provided by the World Bank’s Doing business 2020, which indicates that Vietnam ranks 70th out of 190. Within this ranking, in terms of ease of doing business, Vietnam ranks 115th, while in terms of facilities for cross-border trade, its position is 104th.
A country open to trade
Vietnam has been a member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) since 1995, a circumstance that has led to good trade relations with its member countries (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand), but also with other neighboring countries, such as China (second largest trading partner), Japan (third) and Korea (fourth), although its main customer is the United States.
On the other hand, with the incorporation of Vietnam into the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2006, the country’s relations with the rest of the world opened up rapidly, thanks to an ambitious policy of trade agreements with third countries, after adapting its tariff measures and openness to foreign presence.
One of the main trade agreements that Vietnam has in force is the European Union-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement, in force since 2020. It is a very ambitious and comprehensive agreement because, in addition to facilitating trade exchanges, it includes services, public procurement, intellectual property rights, geographical indications, commitments in international labor standards (ILO) and international environmental agreements.
It should be noted that Vietnam is the European Union’s second largest trading partner in ASEAN, after Singapore, with trade in goods worth €49.3 billion.
Vietnamese exports and imports
With Vietnam’s domestic economic evolution, the composition of its merchandise trade has been transforming. While labor-intensive and low value-added manufactures (textiles and garments, machinery) and food products remain the main exported items, the country has been increasingly moving into the production and export of higher value-added items (electronics and mobile and smart phones).
Imports from Vietnam
In terms of imports, raw materials, machinery and consumer goods continue to stand out. In addition to technology, Vietnam needs to import a good part of the materials necessary to be able to produce in its main industries (textile and wood) and also because consumers, especially those of the growing middle class, demand quality imported products, whether they are household appliances, cell phones, food and beverages or fashion.
According to data provided by ICEX, in 2020 Vietnam’s foreign trade reached a value of 628,000 USM (exports plus imports). Exports, at 348,000 USM, grew by 3.1% over the previous year, while imports, at 280,000 USM, increased by 10.6%.
Exports from Vietnam
Among the exported products, electrical appliances and equipment (153,000 USM and a +58% increase compared to 2019), machines and mechanical appliances (23,871 USM, +82.3%), footwear and parts thereof (23,772 USM, +25.2%), clothing (15,505 USM, +2.3%) and furniture and lamps (15,484 USM, +63.2%) stand out for their volume.
Regarding Vietnamese imports, electrical appliances and equipment (96,041 USM and +23.5% increase compared to 2019), machines and mechanical appliances (26,891 USM, +14.7%) and plastic materials and their manufactures (15,152 USM, -4.5%) stood out. In 2020, the significant decrease in foundry, iron and steel (9,796 USM, -13.6%) and, especially, mineral fuels and oils (8,780 USM, -43.6%) stood out.
Main trading partners of Vietnam
In terms of the country’s trading partners, the United States is the main client, with 23.2% of the total, followed by China (15.7%), the European Union (13.6%), Japan (7.7%) and South Korea (7.5%).
Within the European Union, Vietnamese exports go mainly to the Netherlands (2.6%) and Germany (2.5%); within the rest of the EU (8.4%), Spain receives only 0.1% of Vietnamese exports.
If we look at Vietnam’s imports, the main country sending goods is China, with 29.8%, followed by South Korea (18.5%), Japan (7.7%), Taiwan (6%), the EU (5.8%), the United States (5.7%), Thailand (4.6%), Malaysia (2.9%) and Indonesia (2.3%). There is therefore a dominance of Asian countries as the main suppliers, since they cover more than 80% of Vietnamese imports.
In the case of the European Union, the role of Spain is also very low; Vietnam’s imports from Spain represent 0.2% of the European total.
he European Union buys mainly telecommunications equipment, electronics, textiles (clothing and footwear), furniture and food products (coffee, rice, seafood) from Vietnam.
The EU exports to the Asian country mainly high-tech products, such as machinery and electrical equipment, vehicles and transport equipment, aircraft, pharmaceuticals, chemicals and agricultural products.
As for trade relations between Vietnam and Spain, in 2020 Spanish exports to the Asian country reached €503 M, registering a slight increase of 5% compared to €490 M in 2019. As for Spanish imports from Vietnam, these reflected a decrease of 15% and went from €3,331 M in 2019 to €2,791 M in 2020.
Thus, bilateral relations are scarce, essentially because Spain attaches little importance to the ASEAN countries. And, despite the fact that since 2011 Spain and Vietnam have been treated as strategic partners, Vietnam does not have close relations with Spain, and the treatment given is far from that given to other European countries such as France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands or even Poland.
Information and resources
- Containers
- Customs representation
- Bonded warehouse